git clone https://github.com/jeremypageitcompany/Azure_PA_HA.git
1. What is it Link to heading
- Using native Palo Alto functionality to do high availability with an active-passive setup in Azure
- Deployment of PAs firewall in Azure with IaC Terraform
- Configure a service principal that will do API call to migrate floating IP during failover.
2. Why do this Link to heading
The Good
- No extra component to manage
- Panorama not mandatory to keep rule in sync
- Support Inbound, Outbound, Lateral, IPsec and GP
- HA licence for the Palo Alto are cheaper than standalone licence
The Bad
- Failover takes a long time (~3m)
- Only using performance of 1 firewall
- Not using normal cloud HA mechanisms
3. Diagram Link to heading
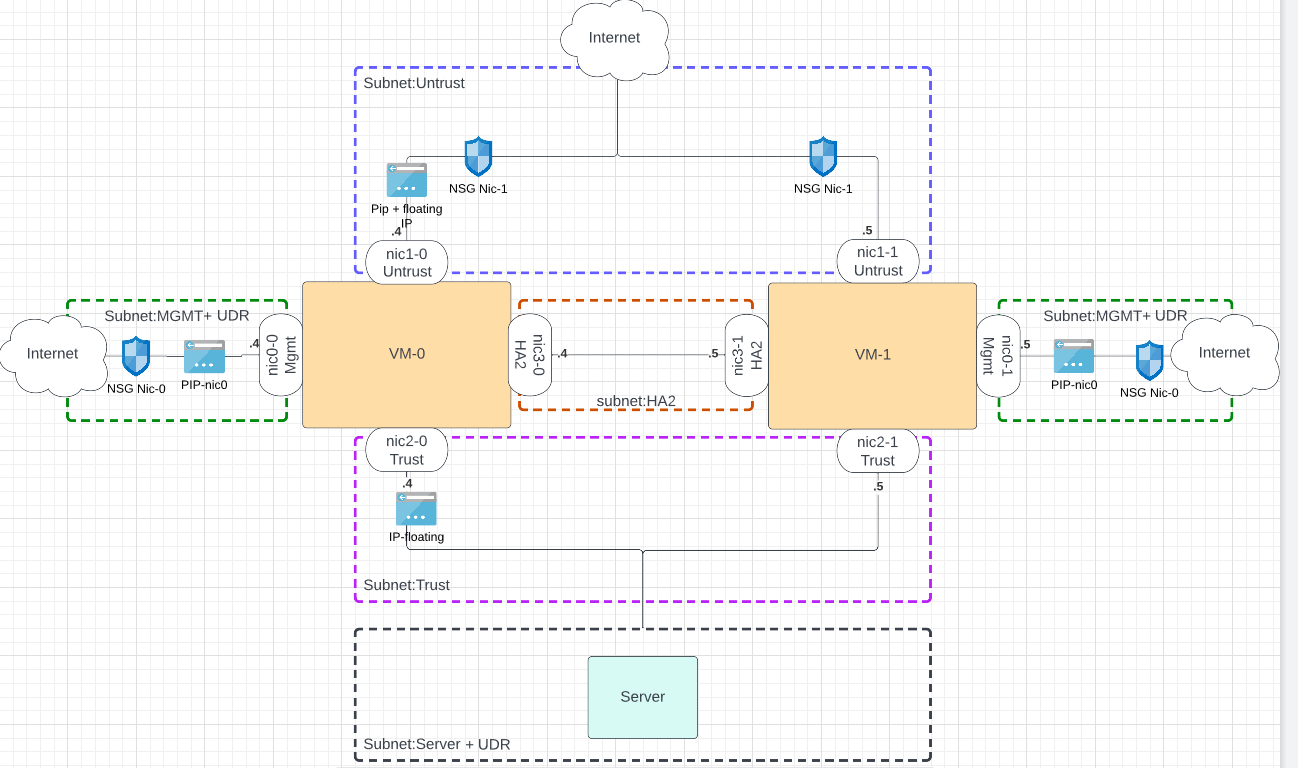
- 2 Palo Alto VM
- 4 nics per VM (mgmt, untrust, trust, ha2)
- Public Ips for each mgmt interfaces and also for the floating IP on the untrust NIC secondary interface
- Secondary interface with floating IP on trust NIC
- Subnet for Servers, with a UDR pointing to the floating Trust IP
4. Lab Link to heading
4.1 Terraform Code Link to heading
git clone the project, go into folder PA_Active-Passive
git clone https://github.com/jeremypageitcompany/Azure_PA_HA.git
cd PA_Active-Passive
some of the variable values you might want to change are in the terraform.tfvars file
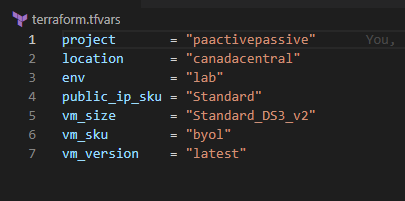
- Project and Env are use in every resource name.
- Location to deploy the resources and its resource group.
- SKU for public IP
- Palo Alto VM size
- Palo Alto SKU, could be byol or licensed (bundle1, bundle2)
- Palo Alto version
vm_password and vm_username are used for the palo altos and the linux VM. They are configured as sensitive variable that will not show in the PLAN but they will show in the state in cleartext.4.2 Terraform deployment Link to heading
- Now do a
terraform initto download plugin and init directory - Then, do a
terraform planto see what will be deploy in Azure terraform applyto push configuration to Azure. TF will ask to enter your username and password that will be set for the PAs and Linux server.
After 5-10 minutes, deployment will be completed.
TF will output the public ips associated with your management interfaces
In you Azure portal, you should now see a new resource group with all associated resources for this project.
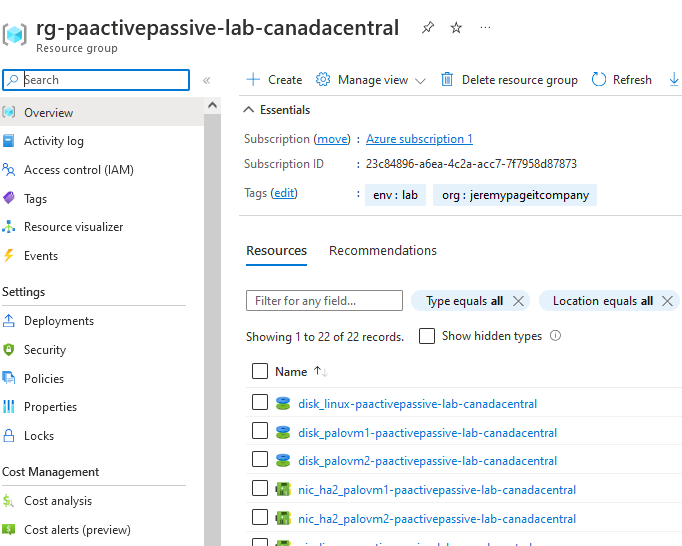
4.2 Palo Alto Configuration Link to heading
4.2.1 Palo HA Link to heading
Log in the GUI of each of your PAs, we will now configure HA.
set up Ethernet1/3 on each as HA type
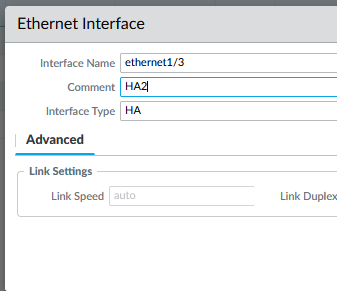
now go into the High Availability menu and configure HA settings like this (MGMT ips are used for HA1 communication).
- PA1 HA1 IP:
10.0.0.4 - PA2 HA1 IP:
10.0.0.5
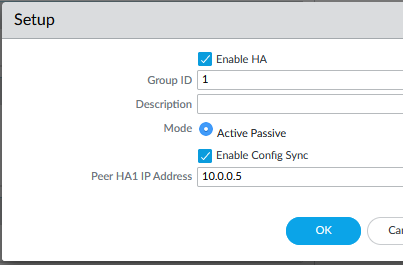
commit the configuration on each.
Now, set up HA communications for the HA2 on each of the firewall.
- PA1 HA2 IP:
10.0.3.4 - PA2 HA2 IP:
10.0.3.5
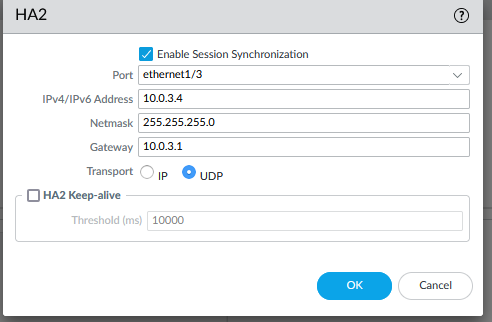
commit the configuration on each.
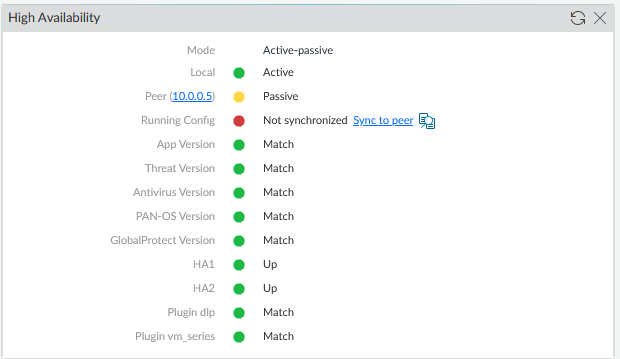
Validate result (Dashboard, add widget High Availability)
Click on Sync to peer on the active firewall.
4.2.2 Layer 3 Link to heading
Now we will configure the interfaces, route and policy on the active peer.
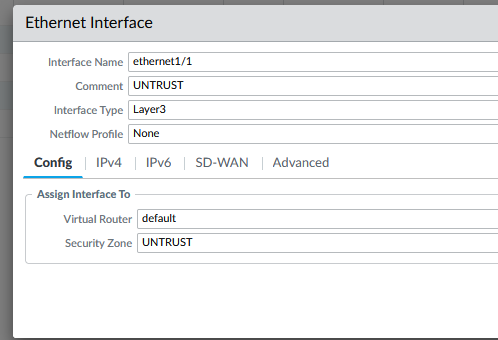
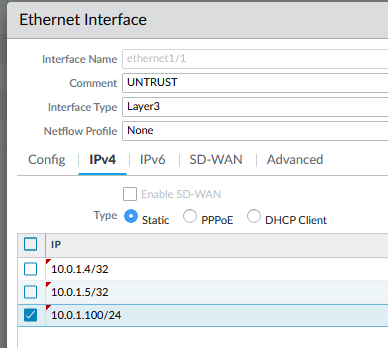
UNTRUST interface
- ethernet1/1
- Type: Layer3
- VR: default
- Zone: Create one, call it UNTRUST
- IP: 10.0.1.4/32, 10.0.1.5/32, 10.0.1.100/24
- Add a mgmt profile that allow PING
TRUST interface
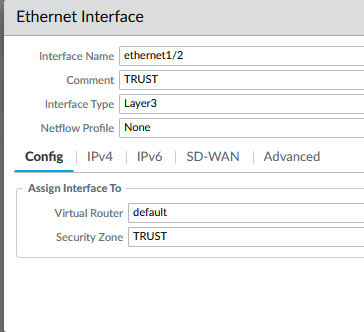
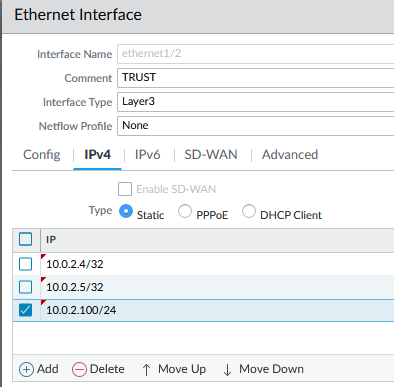
- ethernet1/2
- Type: Layer3
- VR: default
- Zone: Create one, call it TRUST
- IP: 10.0.2.4/32, 10.0.2.5/32, 10.0.2.100/24
- Add a mgmt profile that allow PING
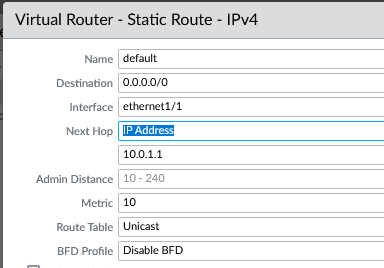
DEFAULT static route
- Name: Default
- Destination: 0.0.0.0/0
- Interface: ethernet1/1
- Next hop IP: 10.0.1.1 (Azure gateway subnet)
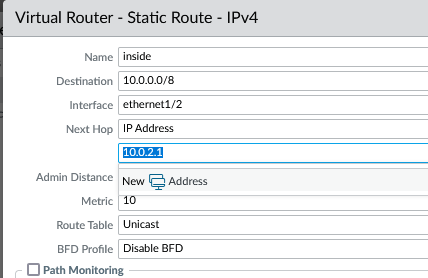
INSIDE static route
- Name: Inside
- Destination: 10.0.0.0/8
- Interface: ethernet1/2
- Next hop IP: 10.0.2.1 (Azure gateway subnet)
Security Policy
- Name: Outbound-Server
- Source Zone: TRUST
- Destination Zone: UNTRUST
- Action: Allow

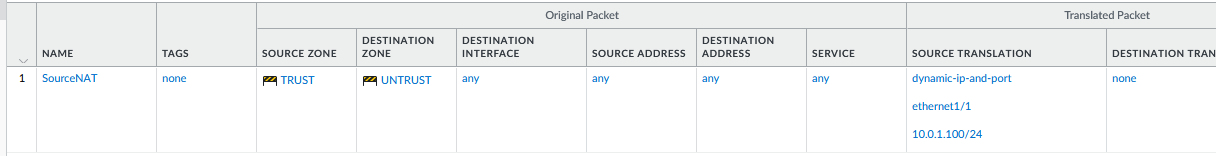
NAT Policy
- Name: SourceNAT
- Source Zone: TRUST
- Destination Zone: UNTRUST
- Source translation: Dynamic IP and Port, ethernet1/1 , 10.0.1.100/24 (The floating IP)
4.2.3 Azure HA Link to heading
To allow Palo Alto to interact with Azure during a failover, a Service Principal is required.
You first need to register an App in Azure AD (Register an application)
Then go to your subscription and assign it a role of Contributor
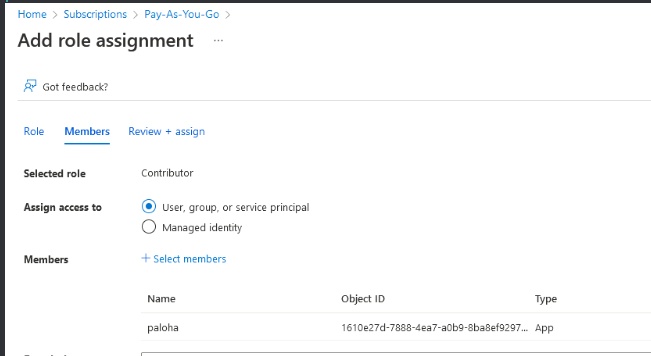
Go to your application and add it a Secret
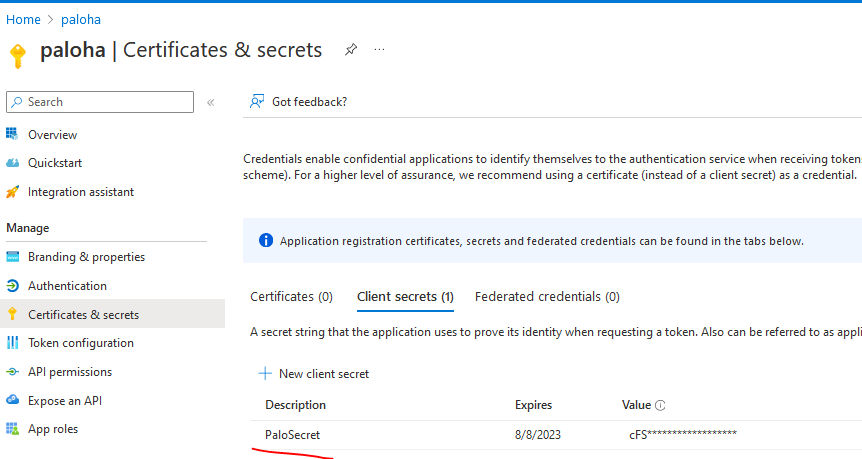
Now take note of the following information in Azure, you will need it on the Palo:
- App Client ID
- App Tenant ID
- Subscription ID
- Resource Group Name
- Secret Key of the App
Go to the Palo, in Device - VM-Series and add an Azure HA Configuration
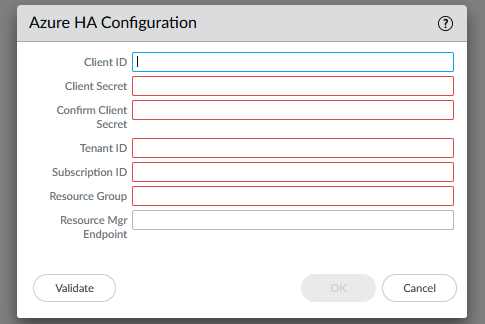
fill this up and commit the configuration.
5. Test Failover Link to heading
We will test failover by doing the following:
- Connect SSH to palo mgmt
- jump to linux device in SSH
- Initiate a PING to the internet from linux device
- Validate in PA log that traffic is allowed/nat and PING working.
- Initiate a Failover on PA
- Validate floating IPs are being transfered to secondary PA
- Validate PING is working again.
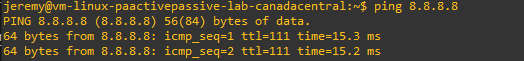
Connect in SSH to Palo and do the following ssh host 10.0.100.4
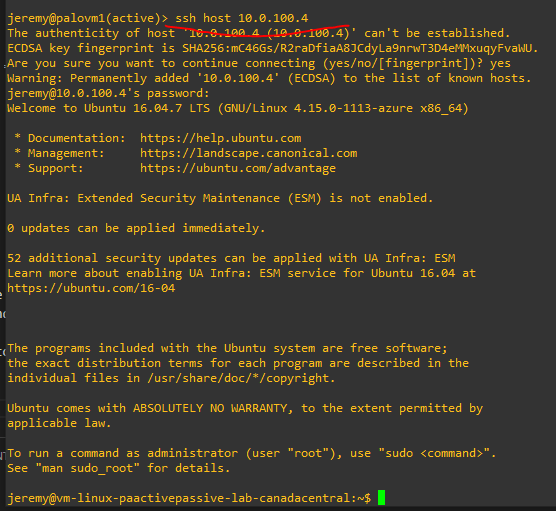
Starts a continous PING to 8.8.8.8, validate all is working as expected on PA
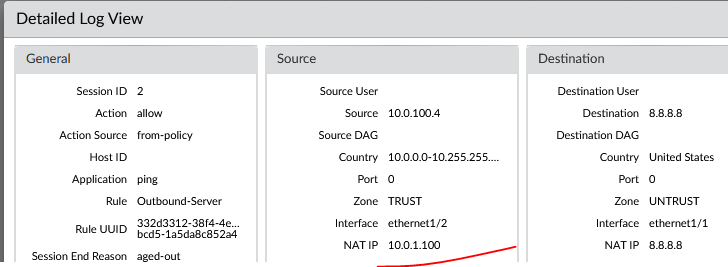
Check PA log, you should see traffic being source NAT to TRUST floating IP 10.0.1.100
you can also check that your using the correct public IP associated with the UNTRUST floating IP curl icanhazip.com
Now initiate a failover in: Device - High Availability - Operational Commands
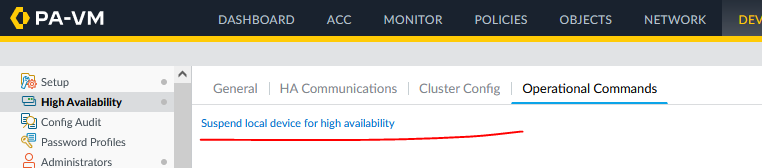
Now your other PA should be the Active peer, Ping will drop until Azure move floatings IPs.
The end result expected in Azure is that the floating IP will be move to the TRUST/UNTRUST nic of palovm2
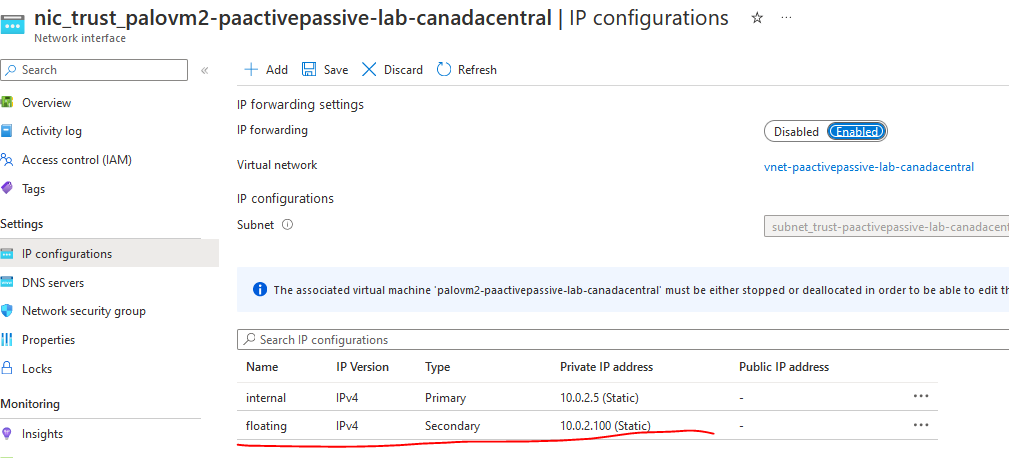
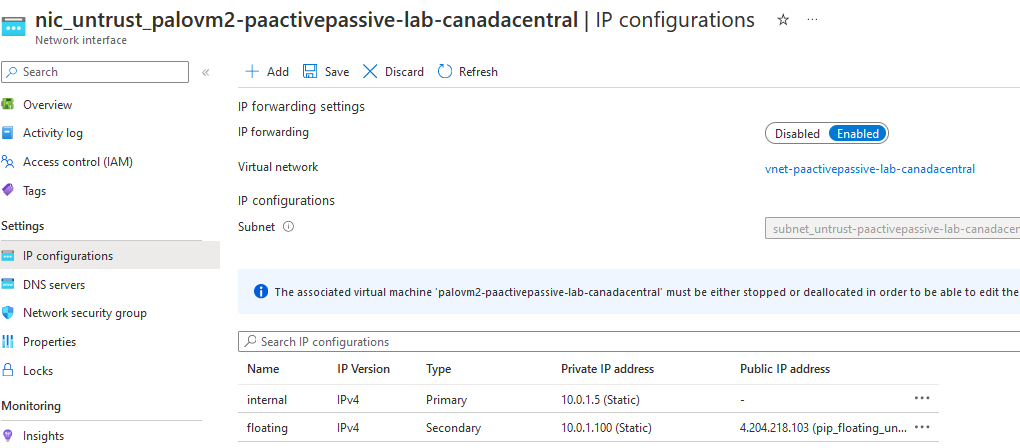
After that, PING will start to work again, traffic is passing throught the secondary PA.